Causes of wisdom tooth extraction
The third group of molar teeth, called wisdom teeth, grow between the ages of 17 and 21. Teeth are classified according to location and function. Sharper teeth can break food into smaller pieces and smooth teeth can eat food.
Wisdom teeth are straight teeth called molars or mill teeth. The mill teeth are at the end of the mouth.
The first set of teeth grows from infancy to early adolescence. These teeth are lost in early adolescence. Then, after a short pause, permanent teeth begin to grow. In early adulthood, the last group of teeth, the wisdom teeth, appear.
At what age do wisdom teeth grow?
Initially, a set of 20 deciduous teeth grows and disappears. Then 32 permanent teeth grow. The first set of molar teeth usually appears at the age of 6, the second set around the age of 12, and the final set, which are wisdom teeth, shortly after the age of 21.
Psychologists believe that man has evolved beyond the need for wisdom teeth. Therefore, in some people, wisdom teeth may never grow. In addition, in some people, wisdom teeth are present under the gums but do not grow.
In such cases, X-rays can confirm the presence of wisdom teeth under the gums. In any case, wisdom teeth can cause many oral health problems.
Causes of wisdom tooth extraction
Human jaws get smaller over time. This evolutionary development may occur for a variety of reasons. Smaller jaws mean that there is not enough space for teeth to grow. There are a total of 4 wisdom teeth, two of which grow in the maxilla and two in the mandible.
Insufficient space for wisdom teeth to grow leads to many problems, including the following:
- Crooked teeth
- Crowded teeth
- Wisdom teeth grow transversely
- Increased tooth decay
- Jaw pain
- Cysts under the gums and possibly a tumor
In case of any of the above changes, the dentist recommends pulling and extracting wisdom teeth. Adolescents should be evaluated surgically to remove wisdom teeth. The recovery process from wisdom tooth surgery is easier and better at a young age and before the complete formation of roots and bones.
Extraction of wisdom teeth also prevents the onset of possible problems. In addition, doctors sometimes recommend that wisdom teeth be extracted before any orthodontic treatment, such as the installation of brackets, to prevent deformity of the jaw and teeth.
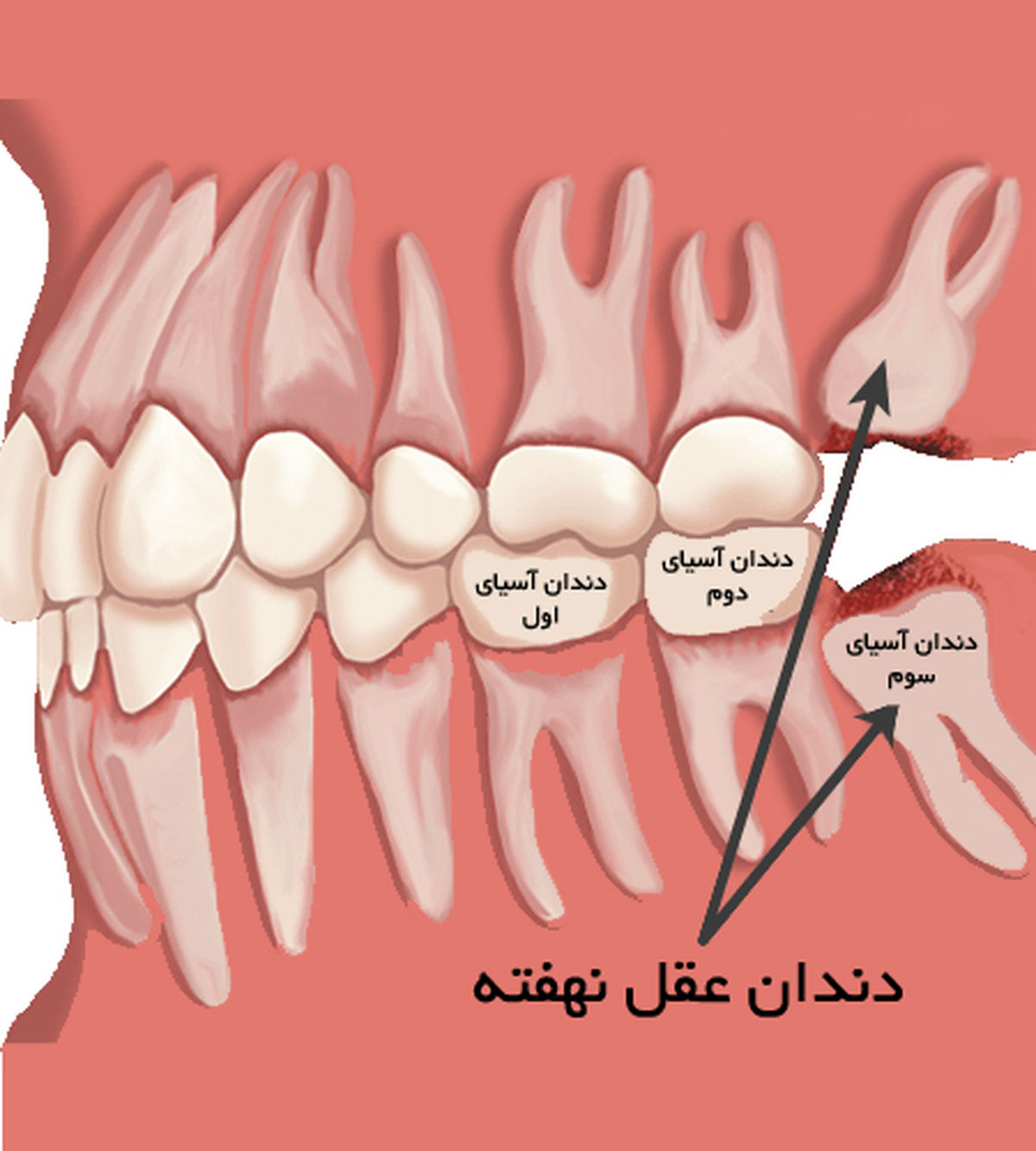
The wisdom teeth are hidden
If the wisdom tooth remains under the gums or does not have enough space to break the gums, it is called a wisdom tooth. Impacted wisdom teeth can lead to pain, damage to other teeth and other dental problems.
In some cases, impacted wisdom teeth may not be an obvious or immediate problem, but because they are difficult to clean, they may be more vulnerable to tooth decay and gum disease than other teeth. An impacted wisdom tooth that causes pain or other dental complications is usually extracted.
Symptoms of latent wisdom teeth
Some people will have no problem with impacted wisdom teeth. While others may experience obvious symptoms. An impacted wisdom tooth may break a portion of the gum and grow to the point where it is called an incomplete wisdom tooth. This condition can cause food to become trapped and difficult to clean.
In some people, a defective wisdom tooth can be very painful. If the tooth becomes infected or causes other problems, the symptoms may include the following:
- Pain or swelling around the jaw
- Redness of the gums, swelling or bleeding
- Bad Breath
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth
- Difficulty opening your mouth
In other cases, the damaged tooth may never grow, which is called a completely impacted wisdom tooth.
What causes occult wisdom teeth?
What causes impacted wisdom teeth? Wisdom teeth may not grow normally due to lack of space. In some people, these teeth grow without any problems and line up with other mill teeth.
However, in many cases, the mouth is too crowded and the third molars can not grow normally. In addition, wisdom teeth may grow incorrectly and angularly, leading to incomplete wisdom teeth.
Complications of latent wisdom teeth
Impacted wisdom teeth can cause many problems in the mouth, including:
- Damage to other teeth: If the wisdom tooth presses on the second molar, it may cause damage to it. This pressure can also cause congestion in other teeth, which requires orthodontic treatment to straighten.
- Cysts: Wisdom teeth form in sacs inside the jawbone. This sac can fill with fluid and form a cyst that damages the jawbone, teeth and nerves. In rare cases, wisdom teeth develop non-cancerous tumors. In this condition, tissue and bone need to be removed.
- Caries: It seems that wisdom teeth that have grown to some extent are more at risk of caries than other teeth. This is because wisdom teeth are difficult to clean and food and bacteria are easily trapped between the gums and the half-protruding teeth.
- Gum disease: Problems cleaning incomplete wisdom teeth increase the risk of a painful and inflammatory gum disease called pericronitis.
Diagnosis of latent wisdom teeth
The dentist can identify impacted wisdom teeth by evaluating the teeth and mouth. These assessments include the following:
- Examine the condition of the teeth and gums
- X-rays that can show the presence of impacted teeth as well as signs of damage to a tooth or bone.
Implanted wisdom tooth surgery
An impacted wisdom tooth that causes pain or other dental problems is usually surgically removed. The process of extracting wisdom teeth includes the following steps:
- Anesthesia injection: The doctor first injects a local anesthetic to numb the site. In some cases, wisdom tooth surgery is performed under general anesthesia.
- Tooth extraction: To extract a tooth, the dentist first makes an incision in the gum. It also removes the bones that block access to the root of the impacted tooth. After removing the tooth, the dentist sutures the wound and fills the empty space with gas.
Extraction of wisdom teeth may cause pain and bleeding as well as swelling of the jaw. In addition, some people have difficulty opening their mouths due to swelling of the jaw muscles.
But these side effects are temporary and go away over time. The dentist will recommend instructions for wound care and control of pain and swelling, such as the use of painkillers as well as cold compresses to reduce swelling.


